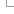ncRNA trees
ncRNA trees are generated by a pipeline that uses a strategy similar to the one used for protein trees, but adapted to the specific characteristics of ncRNAs. This is important because ncRNA genes are well known to form secondary structures where pairs of residues are matched to form loops and other structures. Substitution models that consider pairs of sites have been proposed and implemented in several packages like PHASE or RAxML.
Details on tree building
The ncRNA tree pipeline consists of the following steps:
- Load and identify all the ncRNAs annotated in all the Ensembl genomes.
- Get ncRNA family models from RFAM, taking account of information from mirBase, and classify our ncRNAs into families. Genes with identical ncRNA sequences may be grouped into families at this stage, even in the absence of an RFAM model.
- Families may be expanded with genes that have been projected from a source gene that is already a member of the given family.
- Filter out extra copies in low-coverage assemblies using our EPO multiple alignments.
- Large families that would be too complex to analyse are broken down with QuickTree to limit them to 400 genes.
- Build secondary structure alignments using INFERNAL and refinement of the covariance model.
- Build ncRNA trees with RAxML using 16 different secondary structure models.
- In parallel with the secondary structure alignments and trees, build multiple alignments with PRANK from the genomic sequences of the ncRNAs. For these alignments we include the flanking region of the genes (twice the length of the gene at each side). Where possible, we also store the unflanked alignment, which serves as the main alignment of the gene tree if no secondary structure alignment is available.
- With the genomic alignments, build a neighbour-joining (NJ) and a maximum-likelihood (ML) tree using TreeBeST.
- For very big families, build fast and efficient trees using FastTree and RAxML-Light.
- For each family, add the species tree to the set of trees already obtained and reconcile them all using TreeBeST, obtaining one final tree for the given family.
Gene tree building in Murinae and Pig breeds
When inferring ncRNA trees for Mouse strains and Pig breeds, the EPO multiple alignment filter is not applied.
Additionally, gene trees and homologies may be excluded if they consist entirely of genes that are present in another gene-tree collection.
References
ncRNA orthologies in the vertebrate lineage. Miguel Pignatelli, Albert J. Vilella, Matthieu Muffato, Leo Gordon, Simon White, Paul Flicek, Javier Herrero. Database (Oxford) 2016 pii:bav127.