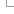Ensembl Variation - Variant classification
Sequence variants
| Type | Description | Example (Reference / Alternative) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism | Ref: ...TTGACGTA... |
Alt: ...TTGGCGTA... |
| Insertion | Insertion of one or several nucleotides | Ref: ...TTGACGTA... |
Alt: ...TTGATGCGTA... |
| Deletion | Deletion of one or several nucleotides | Ref: ...TTGACGTA... |
Alt: ...TTGGTA... |
| Indel | An insertion and a deletion, affecting 2 or more nucleotides | Ref: ...TTGACGTA... |
Alt: ...TTGGCTCGTA... |
| Substitution | A sequence alteration where the length of the change in the variant is the same as that of the reference. | Ref: ...TTGACGTA... |
Alt: ...TTGTAGTA... |
Structural variants
| Type | Description | Example (Reference / Alternative) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNV | Copy Number Variation: increases or decreases the copy number of a given region | Reference: |
"Gain" of one copy: "Loss" of one copy: |
| Inversion | A continuous nucleotide sequence is inverted in the same position | Reference: |
Alternative: |
| Translocation | A region of nucleotide sequence that has translocated to a new position | Reference: |
Alternative: |
Variant classes
We call the class of a variant according to its component alleles and its mapping to the reference genome, and then display this information on the website. Internally we use Sequence Ontology terms, but we map these to our own 'display' terms where common usage differs from the SO definition (e.g. our term SNP is closer to the SO term SNV). All the classes we call, along with their equivalent SO term, are shown in the table below. We also differentiate somatic mutations from germline variants in the display term, prefixing the term with 'somatic'. If you are working with the API, you can fetch either the SO term or the display term.
| * | SO term | SO description | SO accession | Called for (e.g.) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNV | SNVs are single nucleotide positions in genomic DNA at which different sequence alternatives exist. | SO:0001483 |
|
||
| substitution | A sequence alteration where the length of the change in the variant is the same as that of the reference. | SO:1000002 |
|
||
| Alu_deletion | A deletion of an Alu mobile element with respect to a reference. | SO:0002070 |
|
||
| Alu_insertion | An insertion of sequence from the Alu family of mobile elements. | SO:0002063 |
|
||
| HERV_deletion | A deletion of the HERV mobile element with respect to a reference. | SO:0002067 |
|
||
| HERV_insertion | An insertion of sequence from the HERV family of mobile elements with respect to a reference. | SO:0002187 |
|
||
| LINE1_deletion | A deletion of a LINE1 mobile element with respect to a reference. | SO:0002069 |
|
||
| LINE1_insertion | An insertion from the Line1 family of mobile elements. | SO:0002064 |
|
||
| SVA_deletion | A deletion of an SVA mobile element. | SO:0002068 |
|
||
| SVA_insertion | An insertion of sequence from the SVA family of mobile elements. | SO:0002065 |
|
||
| complex_chromosomal_rearrangement | A contiguous cluster of translocations, usually the result of a single catastrophic event such as chromothripsis or chromoanasynthesis. | SO:0002062 |
|
||
| complex_structural_alteration | A structural sequence alteration or rearrangement encompassing one or more genome fragments, with 4 or more breakpoints. | SO:0001784 |
|
||
| complex_substitution | When no simple or well defined DNA mutation event describes the observed DNA change, the keyword "complex" should be used. Usually there are multiple equally plausible explanations for the change. | SO:1000005 |
|
||
| copy_number_gain | A sequence alteration whereby the copy number of a given regions is greater than the reference sequence. | SO:0001742 |
|
||
| copy_number_loss | A sequence alteration whereby the copy number of a given region is less than the reference sequence. | SO:0001743 |
|
||
| copy_number_variation | A variation that increases or decreases the copy number of a given region. | SO:0001019 |
|
||
| duplication | An insertion which derives from, or is identical in sequence to, nucleotides present at a known location in the genome. | SO:1000035 |
|
||
| interchromosomal_breakpoint | A rearrangement breakpoint between two different chromosomes. | SO:0001873 |
|
||
| interchromosomal_translocation | A translocation where the regions involved are from different chromosomes. | SO:0002060 |
|
||
| intrachromosomal_breakpoint | A rearrangement breakpoint within the same chromosome. | SO:0001874 |
|
||
| intrachromosomal_translocation | A translocation where the regions involved are from the same chromosome. | SO:0002061 |
|
||
| inversion | A continuous nucleotide sequence is inverted in the same position. | SO:1000036 |
|
||
| loss_of_heterozygosity | A functional variant whereby the sequence alteration causes a loss of function of one allele of a gene. | SO:0001786 |
|
||
| mobile_element_deletion | A deletion of a mobile element when comparing a reference sequence (has mobile element) to a individual sequence (does not have mobile element). | SO:0002066 |
|
||
| mobile_element_insertion | A kind of insertion where the inserted sequence is a mobile element. | SO:0001837 |
|
||
| novel_sequence_insertion | An insertion the sequence of which cannot be mapped to the reference genome. | SO:0001838 |
|
||
| short_tandem_repeat_variation | A variation that expands or contracts a tandem repeat with regard to a reference. | SO:0002096 |
|
||
| tandem_duplication | A duplication consisting of 2 identical adjacent regions. | SO:1000173 |
|
||
| translocation | A region of nucleotide sequence that has translocated to a new position. The observed adjacency of two previously separated regions. | SO:0000199 |
|
||
| deletion | The point at which one or more contiguous nucleotides were excised. | SO:0000159 |
|
||
| indel | A sequence alteration which included an insertion and a deletion, affecting 2 or more bases. | SO:1000032 |
|
||
| insertion | The sequence of one or more nucleotides added between two adjacent nucleotides in the sequence. | SO:0000667 |
|
||
| sequence_alteration | A sequence_alteration is a sequence_feature whose extent is the deviation from another sequence. | SO:0001059 |
|
||
| probe | A DNA sequence used experimentally to detect the presence or absence of a complementary nucleic acid. | SO:0000051 |
|
||
* Corresponding colours for the Ensembl web displays (only for Structural variants). The colours were originally based on the dbVar displays.
Human variant class distribution - Ensembl 115
Insertion and Deletion coordinates
In Ensembl, an insertion is indicated by start coordinate = end coordinate + 1. For example, an insertion of 'C' between nucleotides 12600 and 12601 on the forward strand is indicated with start and end coordinates as follows:
12601 12600
A deletion is indicated by the exact nucleotide coordinates. For example, a three base pair deletion of nucleotides 12600, 12601, and 12602 of the reverse strand will have start and end coordinates of :
12600 12602